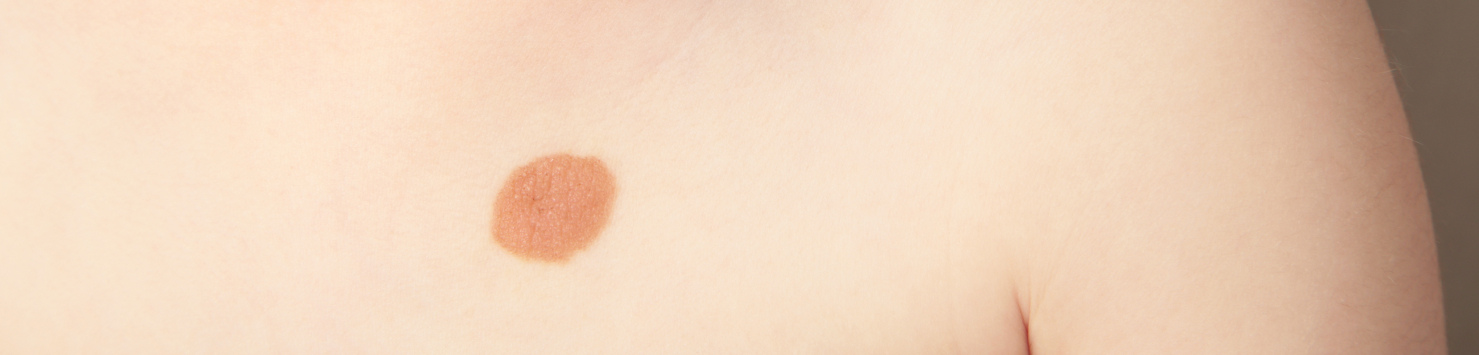
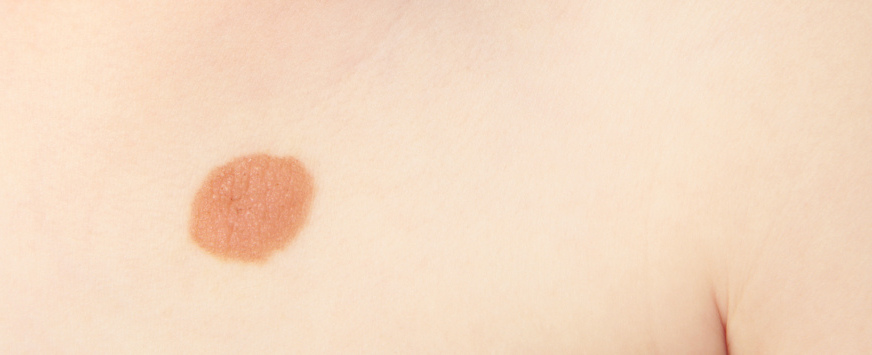
A birthmark is a type of skin discoloration or abnormality that is present at birth or appears shortly after. Birthmarks can vary in size, shape, color, and location on the body. They are typically harmless and do not require medical treatment unless they cause functional impairment or significant cosmetic concerns.
Birthmarks
Types
Vascular birthmarks
These birthmarks are caused by abnormal blood vessels in the skin. They can appear red, pink, purple, or blue in color and are often flat or raised. Examples of vascular birthmarks include: Salmon patches (also known as “angel’s kisses” or “stork bites”): These birthmarks are usually pink or red and appear on the forehead, eyelids, upper lip, or back of the neck. They often fade over time.
Pigmented birthmarks
Pigmented birthmarks occur due to an overgrowth or clustering of pigment-producing cells in the skin. They can range in color from tan to brown to black. Examples of pigmented birthmarks include:
- Café-au-lait spots: These birthmarks are light brown in color and typically have smooth, well-defined edges. They can vary in size and may increase in number over time.
- Mongolian spots: Mongolian spots are bluish-gray birthmarks that commonly appear on the lower back or buttocks of individuals with darker skin tones. They usually fade gradually over several years.
Hemangiomas
are raised, red or purplish birthmarks caused by an overgrowth of blood vessels. They can be superficial (capillary hemangiomas) or deeper (cavernous hemangiomas).
Hemangiomas may initially appear small and then grow rapidly during the first few months of life. Most hemangiomas shrink and fade over time, but some may require medical intervention.
Congenital melanocytic nevi
These are larger, dark brown or black birthmarks that are caused by an overgrowth of pigment-producing cells. They can vary in size and shape and may have a rough or bumpy texture. Larger congenital melanocytic nevi may have an increased risk of developing into skin cancer later in life.
These are larger, dark brown or black birthmarks that are caused by an overgrowth of pigment-producing cells. They can vary in size and shape and may have a rough or bumpy texture. Larger congenital melanocytic nevi may have an increased risk of developing into skin cancer later in life.
Recommendations
Recommendations for birthmarks depend on the specific type and characteristics of the birthmark. While most skin blemishes do not require treatment and tend to fade or become less noticeable over time, certain situations may warrant medical intervention or monitoring. Here are some general recommendations:
Regular
monitoring
Keep an eye on the birthmark’s size, shape, color, and any changes over time. Take note of any rapid growth, bleeding, pain, or other concerning symptoms. This can help detect any potential issues or determine if further evaluation is necessary.
Sun
protection
Regardless of the type of birthmark, it’s important to protect the skin from excessive sun exposure. Sunscreen with a high SPF should be applied to the birthmark and surrounding skin when exposed to the sun. Wearing protective clothing, such as hats and long-sleeved shirts, and seeking shade can also help minimize sun damage and potential changes in the birthmark’s appearance.
Consultation with a
healthcare professional
If you have any concerns about a birthmark, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or pediatrician, for a proper evaluation and guidance. They can provide a thorough examination, determine the type and characteristics of the skin blemishes, and advise on the need for further treatment or monitoring.
Education
and support
It can be beneficial to educate yourself about the specific type of birthmark, its natural course, and available treatment options. Support groups or online communities may provide additional information, resources, and a platform to connect with others who have similar experiences.
Cosmetic
considerations
If a birthmark is causing significant cosmetic concerns or affecting a person’s self-esteem, there may be options for cosmetic treatments. These can include laser therapy, surgical removal, or camouflage techniques, depending on the type and location of the skin blemishes. Consultation with a dermatologist or plastic surgeon who specializes in birthmark treatments can provide personalized recommendations.
The recommendations for birthmarks can vary depending on the individual case. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance tailored to your specific situation.