Warts are usually harmless, but they can be bothersome or cosmetically undesirable. Some warts may resolve on their own over time, while others may persist or multiply.
Wart (Verruga)
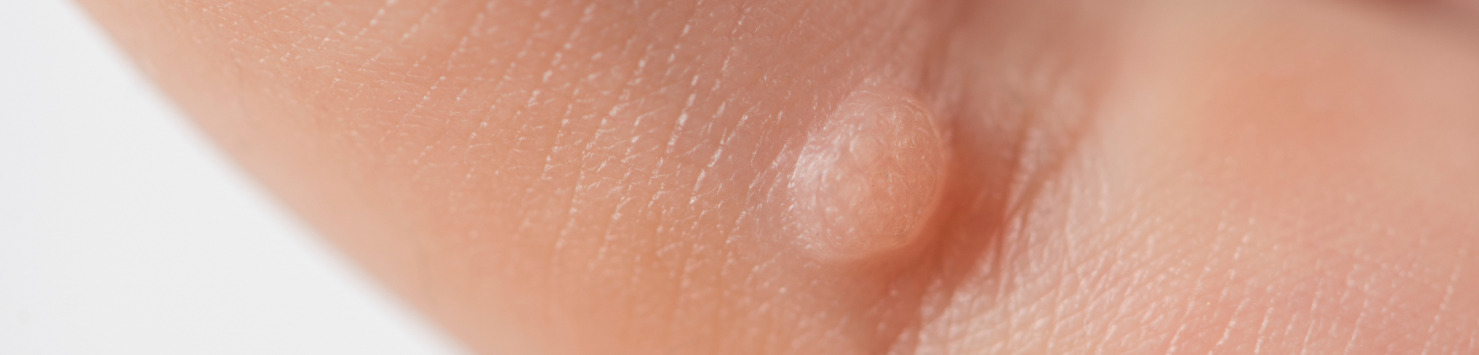
A wart, also known as a verruca, is a common skin growth caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Moreover, warts can appear on various parts of the body, including the hands, feet, face, and genitals. Typically, they have a rough texture and can vary in size, shape, and color.
In addition, warts are contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces or objects. Furthermore, they can spread from one part of the body to another through self-inoculation. For example, scratching or picking at a wart and then touching another area of the skin can cause the virus to spread.


TYPES
Common warts (verruca vulgaris)
These warts commonly appear on the fingers, hands, and around the nails. Typically, they are raised, firm, and have a rough surface. Moreover, common wart verruga often exhibit a cauliflower-like appearance with small black dots, which are clotted blood vessels.
Genital warts
These warts appear on the genital and anal areas and are transmitted through sexual contact. Genital warts can vary in size, shape, and appearance and may be raised, flat, or cauliflower-like. They can be flesh-colored or have a pinkish hue.
Flat warts (verruca plana)
Flat warts are smoother and flatter than other types of warts, often appearing in clusters on the face, arms, or legs. They can be flesh-colored, yellowish, or pink. Flat wart verruga are more common in children and adolescents.
Plantar warts
Plantar warts appear on the soles of the feet and can be painful, especially when walking or standing. Due to the pressure exerted on the feet, plantar wart verruga often grow inward, causing a thick, callus-like layer to form over them. They may have small black dots like common warts.
Treatment
Treatment options for warts include:
Over-the-counter
treatments
Non-prescription wart treatments usually contain salicylic acid, which helps remove the wart gradually. These treatments are available as liquids, gels, or adhesive pads and require regular application.
Cryotherapy
In this procedure, a healthcare professional freezes the wart using liquid nitrogen. The freezing causes the wart to blister and eventually fall off.
Electrosurgery
This procedure involves using an electric current to destroy the wart tissue. It is typically performed under local anesthesia.
Laser therapy
Laser treatment can be used to remove warts by destroying the blood vessels that supply them. It is often reserved for more resistant or recurrent warts.
Immunotherapy
For stubborn or recurrent warts, immunotherapy may be used to stimulate the immune system’s response against the virus. This can involve injecting medications or applying creams to boost the immune system’s ability to fight the wart.

It is important to consult a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist, for a proper diagnosis and guidance on the most appropriate treatment option for your specific case of warts.
Additionally, practicing good hygiene and avoiding direct contact with warts can help prevent their spread.