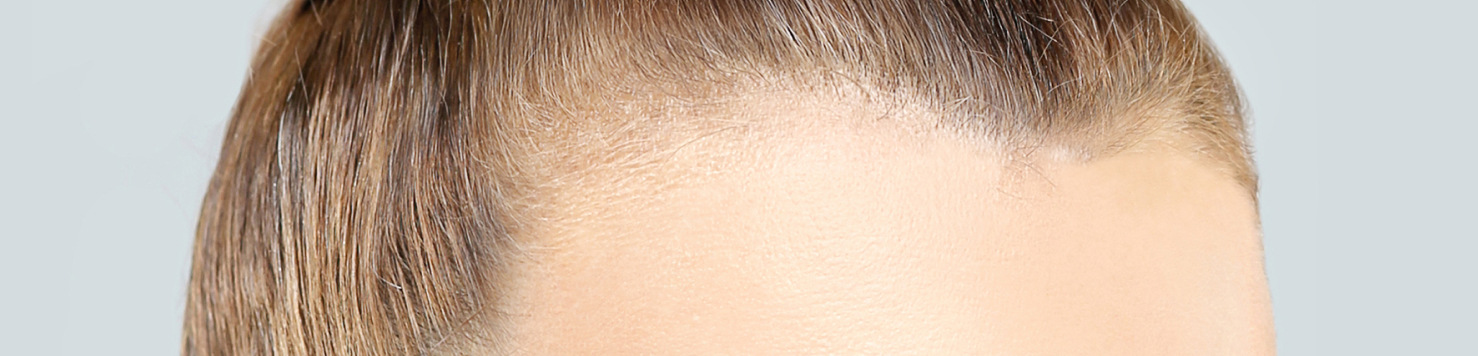
Hair loss often affects a person’s self-esteem and confidence, leading to emotional and psychological challenges. While some types of hair loss are permanent, others may be temporary or reversible with proper treatment.
Hair Loss (Alopecia)
Hair loss, also known as alopecia, refers to the partial or complete loss of hair from areas of the body where hair normally grows. It can affect both males and women and can occur for various reasons, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, medications, or lifestyle factors.
TYPES
Androgenetic alopecia (male/female pattern baldness)
This is the most common form of hair loss, characterized by a progressive thinning of hair on the scalp. In men, it often begins with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, while in women, it typically causes overall hair thinning without significant receding.
Alopecia areata
This is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, resulting in sudden hair loss in patches or across the entire scalp (alopecia totalis). It can also affect other areas of the body, such as the eyebrows, beard, or body hair (alopecia universalis).
Traction alopecia
This form of hair loss is caused by repetitive tension or pulling on the hair, often due to tight hairstyles, braids, ponytails, or the use of hair extensions. It primarily affects the hairline or areas where hair is frequently pulled.
Telogen effluvium
This type of hair loss happens when the hair growth cycle is disrupted, causing excessive shedding. Factors like stress, childbirth, major surgery, severe illness, or certain medications can trigger it.
Alopecia totalis and universalis
These rare forms of alopecia areata cause severe hair loss. Alopecia totalis leads to complete hair loss on the scalp, while alopecia universalis removes all body hair, including eyebrows, eyelashes, and facial hair.
Treatment
Treatment options for hair loss depend on the underlying cause and can include
Medications
Prescription medications, such as minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia), may help slow down hair loss and promote regrowth, particularly in cases of androgenetic alopecia. New oral (Olumiant) immunomodulatory medications are used in the case of Alopecia Areata.
Corticosteroids
Doctors can inject these medicines into the affected areas to reduce swelling and help hair grow back, especially for alopecia areata.
Hair transplant
This surgical procedure involves moving hair follicles from a donor area to the balding or thinning areas of the scalp. It is a long-term solution for hair restoration and can be suitable for individuals with permanent hair loss.
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP)
This method uses a patient’s own blood to create a concentrated plasma with more platelets. Platelets have proteins that help with healing and tissue repair. The blood is spun in a machine to separate the PRP from other parts of the blood.
The plasma is then injected back into the patient’s scalp. The growth factors are thought to boost collagen production and promote hair follicle growth, making it an effective treatment for patients with androgenetic alopecia and telogen effluvium.

Dr. Ciocca is a highly regarded dermatologist and an esteemed researcher who is actively involved as a principal investigator in ongoing clinical trials for phase 2 and 3 of innovative immunomodulatory treatments for Hair Loss.
If you are interested in participating in these promising trials or seeking more information, we encourage you to reach out to our dedicated research team at www.skinresearchsf.com.
They will provide you with the necessary details and assist you professionally throughout the process.
Treatment
In addition to treatments, living a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding too much heat styling or chemicals can improve hair health. Seeing a dermatologist can help find the cause of hair loss and suggest the right treatment.