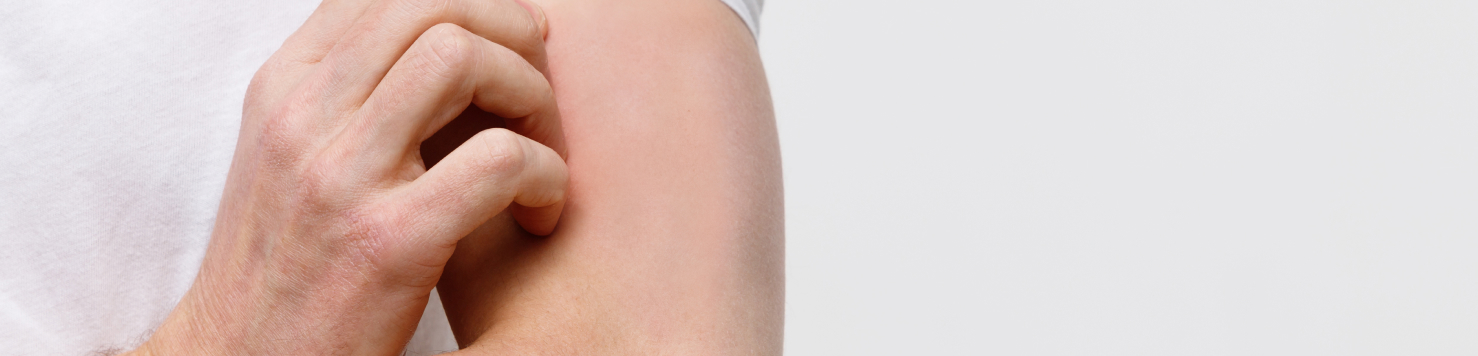
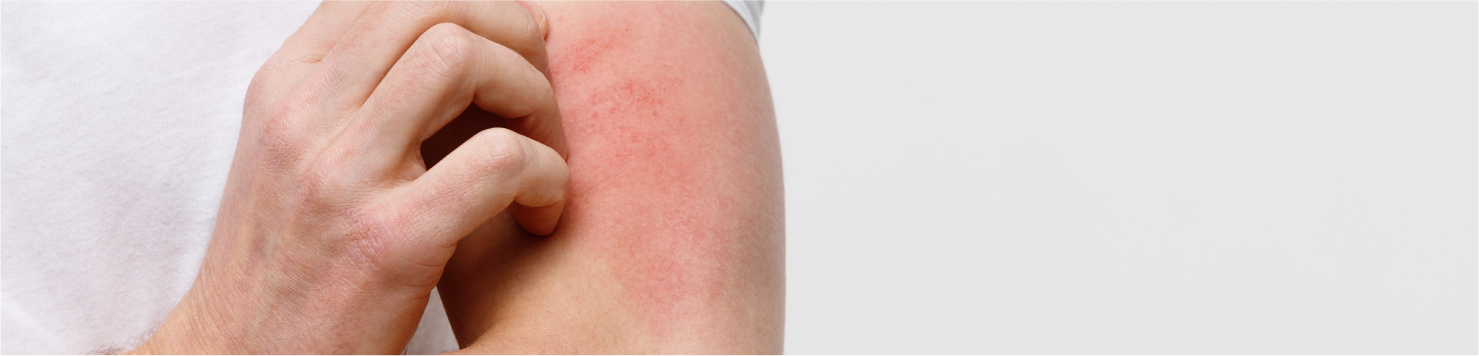
Atopic dermatitis is the predominant form of eczema, which is a skin condition characterized by persistent itching and the development of red patches, typically found on the face, arms, and legs. Although it primarily affects children, it is important to note that it also impacts a significant number of adults, with an estimated 18 million individuals affected.
The hallmark of atopic dermatitis is its cyclical nature; therefore, rashes tend to flare up, subside, and reappear periodically. Moreover, the frequency and severity of these flare-ups vary among individuals. During flare-ups, the skin becomes intensely itchy; consequently, scratching may worsen the condition.
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with a family history of allergies, asthma, or atopic dermatitis itself may be more prone to developing the condition.
Managing atopic dermatitis requires a multifaceted approach; therefore, individuals should focus on relieving symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Moreover, working closely with dermatologists helps create a personalized treatment plan tailored to specific needs. By effectively managing symptoms and reducing flare-ups, individuals can improve their quality of life and find relief from the discomfort of this chronic skin condition.