Key features
Appearance
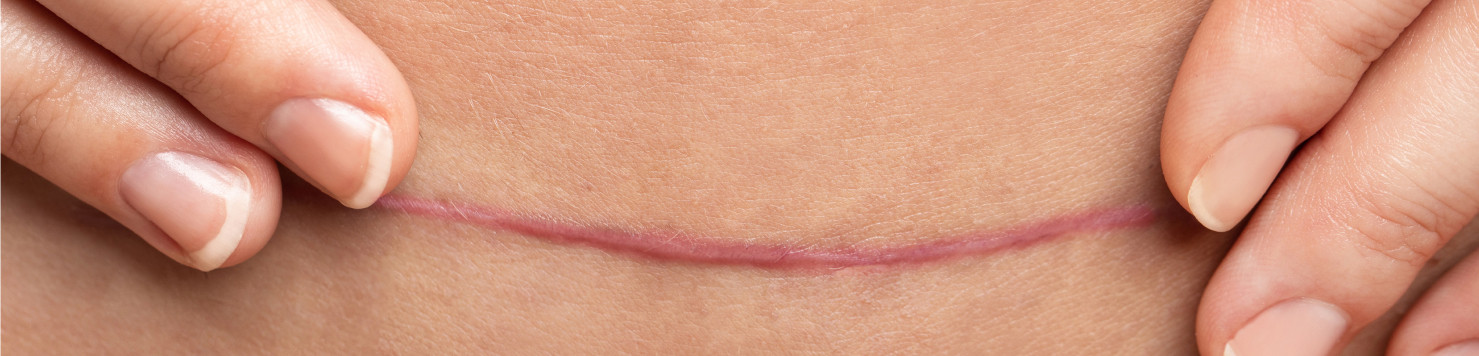
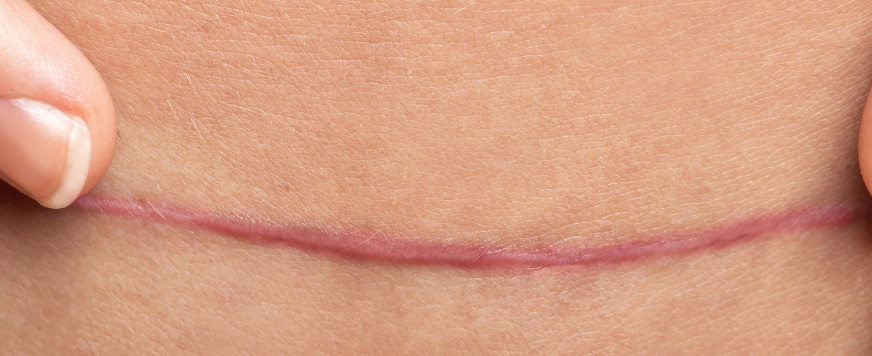
Scars can vary in size, shape, color, and texture. They may appear as flat, raised, indented, or discolored areas on the skin. The color of a scar may range from pink or red during the early stages of healing to a lighter or darker shade compared to the surrounding skin over time.
Healing time
The time it takes for a scar to fully heal varies depending on several factors, such as the size and depth of the wound, individual healing abilities, and proper wound care. Initially, scars may appear red, swollen, or raised, but they usually become less prominent and fade over time.
Texture
Scars can have a different texture than the surrounding skin. They may feel rough, bumpy, or have a shiny or glossy appearance.
Emotional impact
Scars can have both physical and emotional effects on individuals. They may cause self-consciousness, affect body image, and impact self-esteem. Emotional support and counseling may be beneficial for individuals struggling with the psychological impact of Stains.